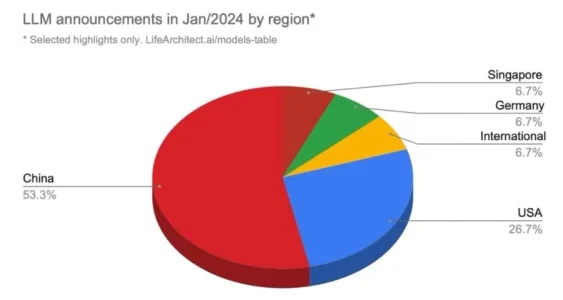
China 6 times ahead of US in GenAI patents, tops with 38,000 filings
Chinese companies lead in GenAI patents, with Tencent topping the list with 2,074 inventions. IBM is the only non-Chinese company in the top five.
Updated: Jul 06, 2024 06:03 AM EST
 Aman Tripathi
Aman Tripathi
GenAI patent filings surge, with image and video data leading the charge.
iStock
Anew United Nations report has revealed that China is significantly ahead in the global race for generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) patents.
The report, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), analyzed GenAI patent filings between 2014 and 2023. It shows that China has filed over 38,000 patents during this period.
Notably, this figure is a staggering six times more than those filed by inventors based in the United States.
GenAI’s Explosive growth and China’s dominance
“Generative AI is a cutting-edge technology that is poised to disrupt various economic, social, and cultural sectors, and it extends far beyond simple human-like text generation using chatbots,” read the report.
It has experienced explosive growth in recent years, and the WIPO report reveals that over 50,000 patent applications related to GenAI have been filed globally in the past decade. Moreover, a quarter of them were submitted in 2023 alone.
The geographic distribution of GenAI patents further underscores China’s dominance in this field. The country boasts 38,210 inventions, dwarfing the US (6,276 patents), South Korea (4,155), Japan (3,409), and India (1,350).
This dramatic lead underscores China’s strategic
focus on AI as a key area of technological development. Subsequently, Chinese companies and institutions dominate the list of top patent applicants, with Tencent Holdings leading at 2,074 inventions, followed by Ping An Insurance (1,564) and Baidu (1,234).
The Chinese Academy of Sciences ranks fourth with 607 inventions, while IBM is the only non-Chinese company in the top five with 601 inventions.
Specific GenAI applications
The report also highlights specific applications of GenAI technology, with
image and video data leading the charge in patent filings, accounting for 17,996 inventions.
Text-based applications follow closely at 13,494 patents, while speech- and music-related inventions total 13,480.
GenAI patents for molecule, gene, and protein-based data have surged as well. Since 2014, 1,494 inventions have been filed, with an average annual growth of 78% over the past five years.
While current applications of GenAI, such as chatbots, are already enhancing customer service experiences, the future holds even more transformative possibilities. From revolutionizing scientific research and drug development to transforming publishing, transportation, and security, GenAI is poised to reshape the global economic landscape.
“GenAI has emerged as a game-changing technology with the potential to transform the way we work, live and play,”
said Daren Tang, WIPO Director General.
The race is on
Currently, GenAI patents make up 6% of total AI patents worldwide. However, the growth in patent filings since the introduction of the deep neural network architecture in 2017 signals an expanding field.
“The number of GenAI patents has increased by over 800%” since 2017, commented the WIPO
report.
The report paints a clear picture that China is currently leading in GenAI patents. However, considering the ever-evolving nature of this technology, it will be safe to surmise that the race for GenAI innovation is far from over.